Enterprise Architecture must have a way to prove its value and worth. The EA Value Measurement techniques provide a series of measurements to illustrate the effectiveness of EA program. The value of EA program can be measured internally and/or externally within the organization. Each measurement area can include a set of metrics that can be gathered to measure the impact of a successful (or unsuccessful) EA program within the enterprise and its ability to achieve its goals. Some of the metrics involve the compliance to standards, project reviews, and architecture consulting hours (Cameron, 2011). The EA measurements must be captured to provide the feedback to stakeholders in EA program. The Metrics and related reports should be pertinent to all stakeholders. Measuring metrics can vary from one organization to another. The EA program exists as decision support organization for CxOs and other decision makers in the organization, it is important to define metrics from their perspective.
Such metrics may include compliance to standards, project reviews, and architecture consulting hours 1. The EA measurements must be captured to provide the feedback to stakeholders in EA program. The Metrics and related reports should be pertinent to stakeholders and must be defined in the EA program charter. Metrics can vary from one organization to another. As EA program exists as decision support organization for CxOs and other decision makers in the organization, it is important to decide on the metrics that will make sense to them. It is very important to decide on metrics in the beginning but the categorization or its alignment to Measurement Area may be adjusted as the population of metric begins.
EA team may establish a measurement matrix for each stakeholder which utilize one or more metric to display relationship with goals and objectives that are important to the stakeholder(s). The metrics should be the statements that elaborate the qualitative or preferably quantitative representation of final measure. 2. The measurement areas and metrics are identified during the planning process.
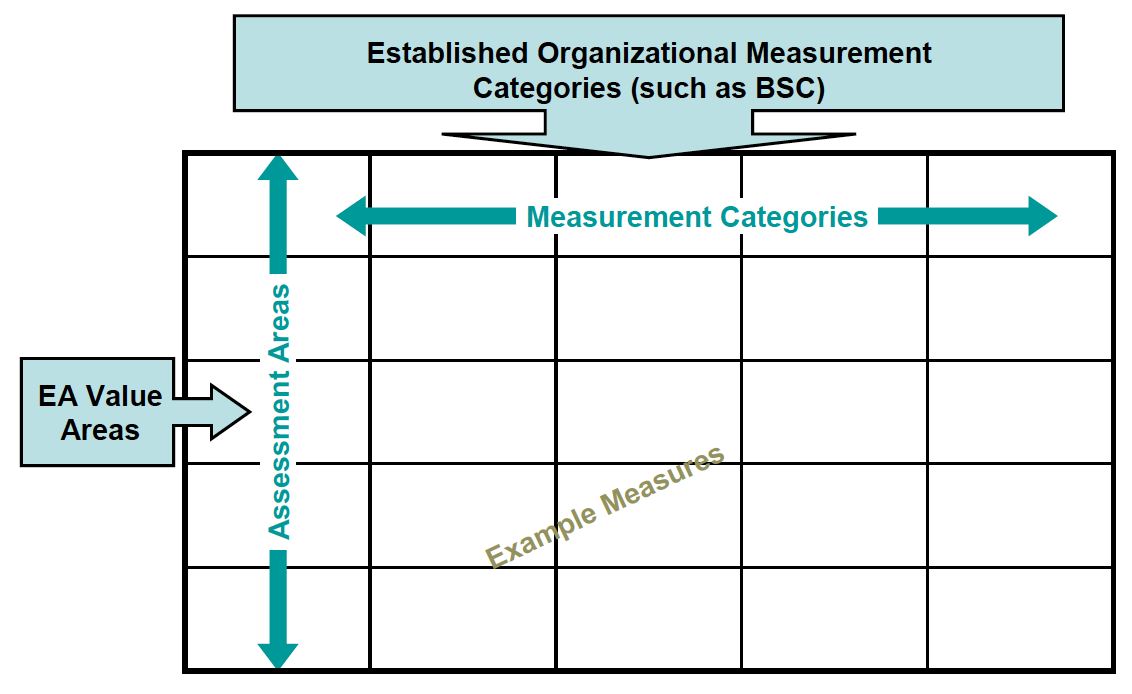
EA Measurement Matrix (Source: Deborah Weiss, Gartner Toolkit, G00142387)
There are several other types of metrics can be captured to assess the health of EA program in an organization based on their needs3.
- Customer Experience metrics that can be captured if it has a direct architectural impact such as User Experience etc.
- Organizational performance metrics
- Productivity and effectiveness metrics like below.
- Reducing time to market for new investments in change
- Integrating and improving business processes across the enterprise (including with partners)
- Improving the ability to integrate data and interfaces across the enterprise (including with external partners)
- Improving the ability to reuse business functions, business processes and application services
- Increasing agility, flexibility, and ability to rapidly change in the event of new strategic scenarios occurring
- Increasing standardization
- Reducing the time taken to develop solutions by maximizing reuse of enterprise architecture models
- Governance and compliance to standards.
- Creating Enterprise Knowledge Base by documenting organizational knowledge for self-support.
- Creation and implementation of Common Vision of Future
- Improvements in Architecture Quality Attributes, such as
- Scalability
- Availability
- Performance
- Efficiency
- Reliability
- Service Level
Organizations must focus on the importance of lessons learned across the performance measurement discipline. The following are the major causes of measurement program failures 4:
- Betting the measurement program on a single metric or trying to find a single metric that would cover a wide range of problems
- Assuming that imitating someone else’s measurements will produce similar outcomes (that is, a quest for industry standards)
- Not linking measures to behaviors to improve decision-making
- Assuming that a set of measures will be valid for all time
- Creating unbalanced measures
- Measuring outputs that can easily be “gamed” or that trigger bad behavior
- Failing to link measures to business benefits or communicate to the business
- Focusing on too narrow a scope of EA team activities
- Lacking commitment to the program or failing to analyze what was collected
- Measuring and committing to improvements in areas outside the EA team’s span of control
- Failing to define the program and data
Successful EA programs are the ones that are visible to its stakeholders and provide evidence of their business value based on solid metrics, scorecards and reporting systems. These will demonstrate the architecture’s impact on IT and business investments and how an architecturally sophisticated approach has mitigated risk or enabled new opportunities to be exploited.
References
- Cameron, B, 2011, EA Value Measurement, Center for Enterprise Architecture, Penn State University
- Weiss, D, Gartner Toolkit, G00142387, Gartner Inc.
- On Enterprise Architecture, 2013, Available at https://ingenia.wordpress.com/2013/06/16/how-to-measure-enterprise-architecture/
- Gartner, 2006, G00143258, Gartner Inc
